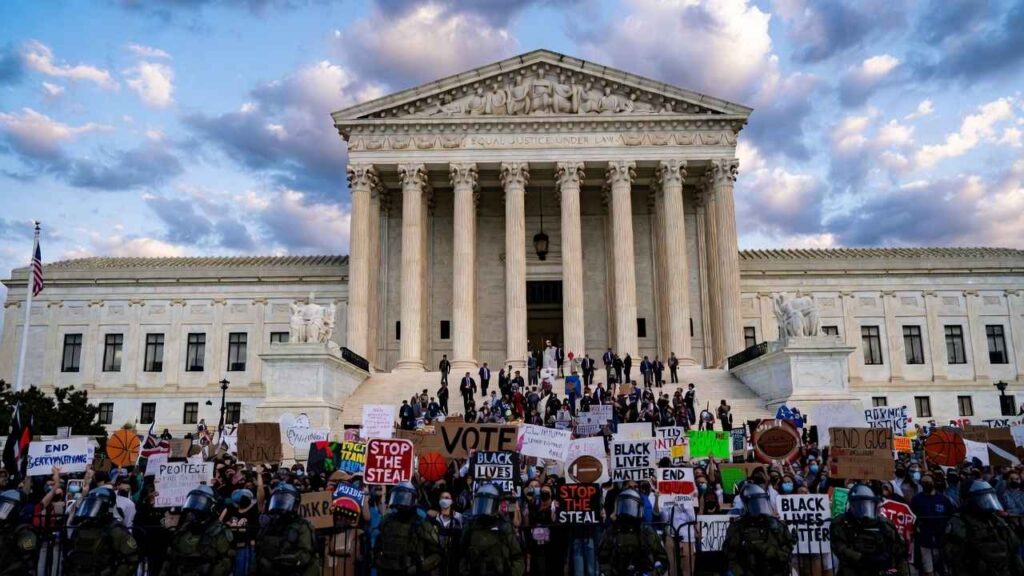
Supreme Court Trans Athletes: The marble steps of the Supreme Court became a battleground this week as justices heard oral arguments in what many are calling the most significant cultural case of 2026. The high court is weighing whether states can legally ban transgender athletes from competing in women’s sports, a question that has divided Americans, sparked passionate protests, and forced justices to grapple with competing visions of fairness, inclusion, and civil rights.
Outside the courthouse, demonstrators from both sides of the issue gathered in large numbers, their chants and signs illustrating the deep divisions this case has created across the country. Inside, the nine justices questioned attorneys for hours, probing the legal, scientific, and constitutional dimensions of state laws that restrict athletic participation based on biological sex.
The outcome of these cases will reverberate far beyond courtrooms and playing fields, potentially reshaping how schools, sports organizations, and governments navigate one of the most contentious issues in American public life.
The Cases Before the Court
The Supreme Court consolidated two separate challenges for this hearing. The first case involves Becky Pepper-Jackson, a 15-year-old student in Idaho who was barred by state law from trying out for her school’s track team. The second case was brought by a West Virginia middle schooler who faced similar exclusion under her state’s law.
Both plaintiffs argue that state bans violate their constitutional rights under the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment and Title IX, the federal law prohibiting sex discrimination in education. Their attorneys contend that excluding transgender girls from girls’ sports is a form of sex discrimination that inflicts serious psychological and social harm on young people who simply want to participate in athletics like their peers.
Idaho and West Virginia defend their laws as necessary protections for cisgender female athletes who they argue face unfair competition from athletes who were assigned male at birth. The states maintain that biological differences in strength, speed, and endurance between males and females justify separate sports categories and that protecting women’s sports is a compelling government interest.
The Legal Arguments: Fairness vs. Inclusion
The central legal question before the Court is whether laws excluding transgender athletes from teams consistent with their gender identity constitute unlawful discrimination or permissible sex-based classification.
Attorneys defending the state bans argued that physical advantages conferred by male puberty, including increased muscle mass, bone density, and cardiovascular capacity, create inherent competitive imbalances. They pointed to scientific research showing that even after hormone therapy, transgender women often retain significant athletic advantages over cisgender women in many sports.
“This isn’t about discrimination,” one state’s attorney argued. “It’s about biology. Women fought for decades to have separate athletic opportunities. These laws protect those opportunities and ensure fair competition.”
Lawyers for the transgender students countered that blanket bans based solely on transgender status are overbroad and unnecessarily exclude young people who pose no competitive threat. They emphasized that sports participation provides crucial benefits for adolescent development, including physical health, social connection, and self-esteem.
“These are children who want to play with their friends,” argued the plaintiffs’ attorney. “The states haven’t shown that these particular students have any unfair advantage, yet they’re categorically excluded based on who they are.”
The Science Debate
Much of the oral argument focused on contested scientific questions about athletic performance, hormone levels, and physical development. Justices pressed both sides on what research actually shows about transgender athletes‘ advantages or disadvantages compared to cisgender competitors.
Defenders of the bans cited studies showing that male puberty produces permanent physical changes that hormone suppression cannot fully reverse. They noted that elite male athletes typically outperform elite female athletes by 10-30 percent in most sports, reflecting fundamental biological differences.
Challengers to the laws pointed to research showing significant variation within both male and female populations and argued that hormone therapy substantially reduces any competitive advantages. They also emphasized that sports governing bodies, including the International Olympic Committee and various national athletic associations, have developed nuanced eligibility criteria rather than categorical bans.
The scientific debate revealed the complexity of the issue. While research shows clear average differences between male and female athletes, there is less consensus about how those differences apply to adolescents who have undergone hormone therapy or who never experienced typical male puberty due to puberty blockers.
The Title IX Question
A crucial aspect of the cases involves the interpretation of Title IX, the 1972 federal law that revolutionized women’s athletics by prohibiting sex discrimination in educational programs receiving federal funding.
State attorneys argued that Title IX explicitly permits sex-separated athletics and that excluding transgender girls from girls’ teams is precisely the type of sex-based classification the law contemplates and allows. They contended that the original purpose of Title IX was to protect opportunities for biological females.
The transgender students’ lawyers countered that Title IX’s protections extend to all forms of sex discrimination, including discrimination based on gender identity. They cited federal agency guidance and lower court rulings finding that discrimination against transgender individuals constitutes sex discrimination under civil rights laws.
The Supreme Court’s ultimate interpretation of Title IX could have sweeping implications beyond athletics, potentially affecting bathroom access, housing assignments, and other sex-separated spaces in schools nationwide.
The Justices’ Concerns
During oral arguments, conservative and liberal justices approached the cases from markedly different perspectives, hinting at how they might ultimately vote.
Conservative justices expressed skepticism about requiring states to allow transgender girls to compete on girls’ teams, focusing on competitive fairness and the purpose of sex-separated sports. Several justices questioned whether allowing transgender participation might discourage cisgender girls from competing or reduce their opportunities for success, scholarships, and recognition.
Justice Samuel Alito posed hypothetical questions about elite competitions and record-breaking performances, asking whether states could reasonably conclude that allowing transgender athletes might undermine women’s sports achievements.
Liberal justices emphasized the dignity interests and equal treatment rights of transgender students. They questioned whether categorical bans were necessary when more tailored approaches might address competitive concerns while still allowing participation. Justice Sonia Sotomayor noted that many transgender girls never go through male puberty and asked whether blanket exclusions unfairly targeted vulnerable young people.
Justice Ketanji Brown Jackson pressed states on whether their laws were carefully crafted to address actual competitive advantages or whether they simply reflected discomfort with transgender identity. She noted that some states allow transgender boys (assigned female at birth) to compete on boys’ teams but prohibit transgender girls from girls’ teams, suggesting potential inconsistency in the rationale.
Broader Cultural Context
The Supreme Court cases arrive amid intense national debate over transgender rights, particularly regarding children and adolescents. Over 20 states have enacted laws restricting transgender athletes from teams consistent with their gender identity, while other states have adopted inclusive policies.
Public opinion polls show Americans are divided, with views often depending on how questions are framed. Many Americans express support for transgender rights generally but also believe biological sex should determine athletic participation. Others view any restrictions on transgender athletes as discrimination that harms vulnerable young people.
The cases have become a flashpoint in broader political battles over parental rights, educational policy, and cultural values. Conservative groups view state bans as common-sense protections for women and girls, while progressive organizations describe them as cruel attacks on transgender youth that perpetuate discrimination and marginalization.
Potential Outcomes and Implications
Legal experts predict the Court will issue its decision before the end of the current term in June 2026. The ruling could take several forms, each with different implications:
A decision upholding the state bans would give states broad authority to restrict transgender athletes and could signal a narrower interpretation of civil rights protections for transgender individuals generally.
A ruling striking down the bans would likely be based on equal protection or Title IX grounds, potentially requiring states to allow transgender participation unless they can demonstrate specific, individualized competitive advantages.
The Court could also issue a narrower ruling that resolves the specific cases without establishing broad nationwide rules, leaving room for different approaches in different jurisdictions.
Whatever the outcome, the decision will shape the landscape for transgender rights litigation for years to come. Beyond athletics, the Court’s reasoning may influence cases involving bathroom access, gender-affirming medical care, identification documents, and other contentious issues at the intersection of transgender rights and traditional sex-based classifications.
Looking Ahead
As the nation awaits the Supreme Court’s decision, schools, athletic associations, and families continue navigating these issues in real time. Some states have already indicated they will adjust their policies based on the Court’s ruling, while others may seek creative workarounds to preserve their preferred approaches.
For the transgender students at the center of these cases, the stakes are deeply personal. They seek not special treatment but simply the opportunity to participate in sports with their peers, to experience the joy of competition and the camaraderie of team membership.
For those who support restrictions, the concern is equally sincere: protecting the opportunities that generations of female athletes fought to secure and ensuring that women’s sports remain competitive spaces where biological females can excel.
The Supreme Court now faces the difficult task of resolving these competing values in a way that respects constitutional principles, acknowledges scientific realities, and considers the human dignity of all involved. The decision, when it arrives, will mark a defining moment in American law and culture, establishing precedents that will govern how we balance fairness, inclusion, and identity for generations to come.